SQL리뷰 수업 코드정리-2
2일차 코드 (서브쿼리 기본)

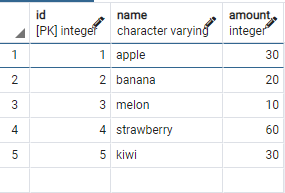
1 | --실제 보유하고 있는 과일 데이터 |
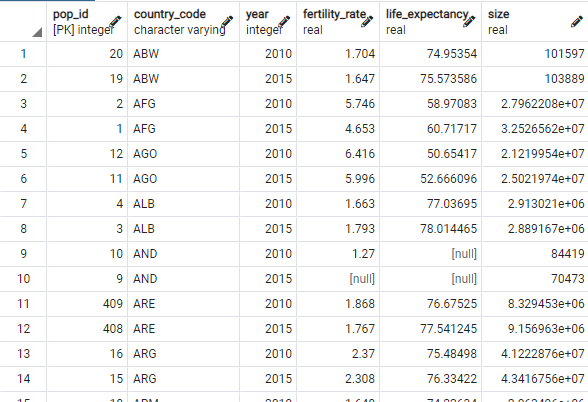
1 | select * from populations; -- 위 테이블 이미지 |
SQL리뷰 수업 코드정리-2
You need to set
install_url to use ShareThis. Please set it in _config.yml.